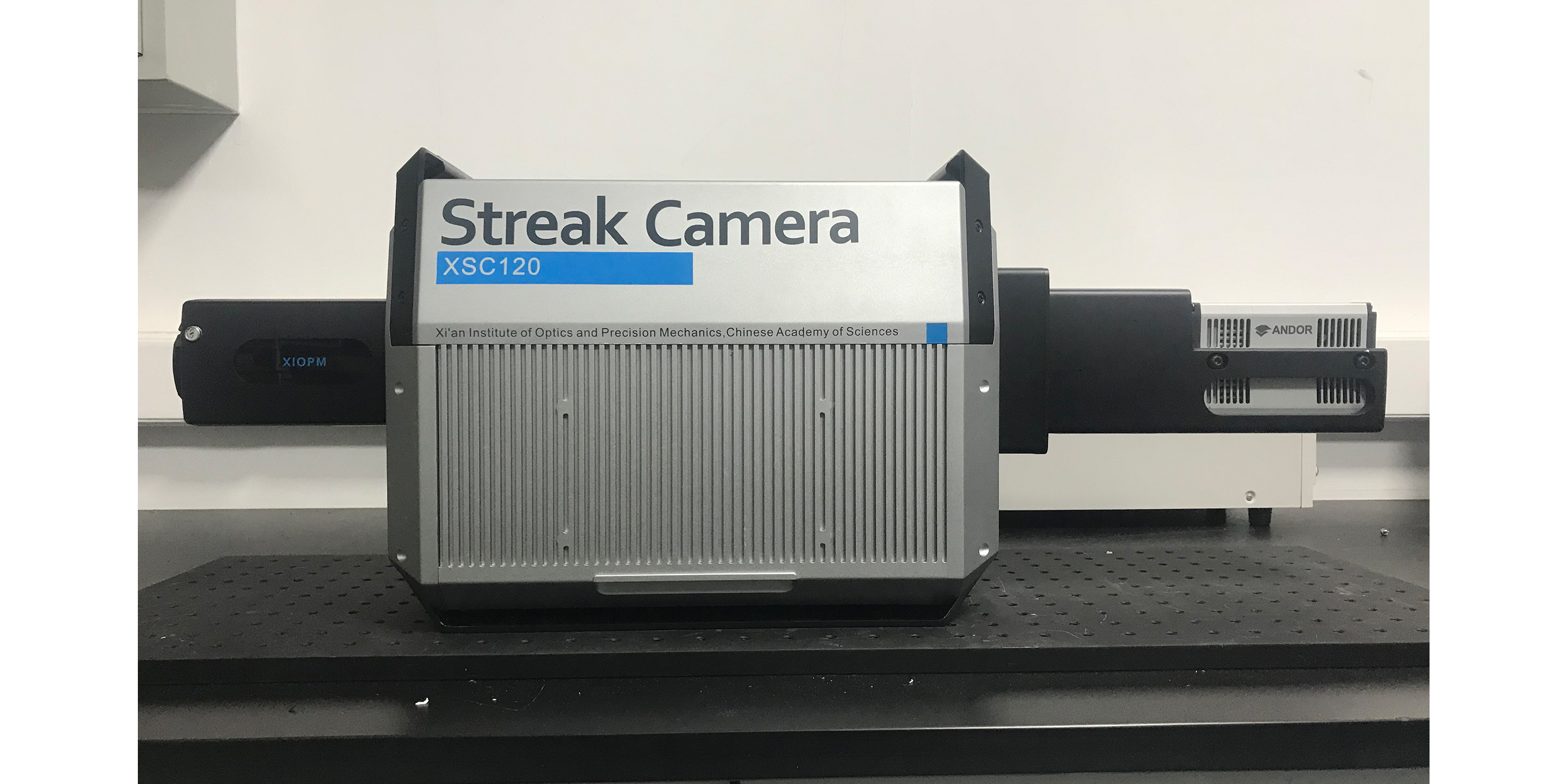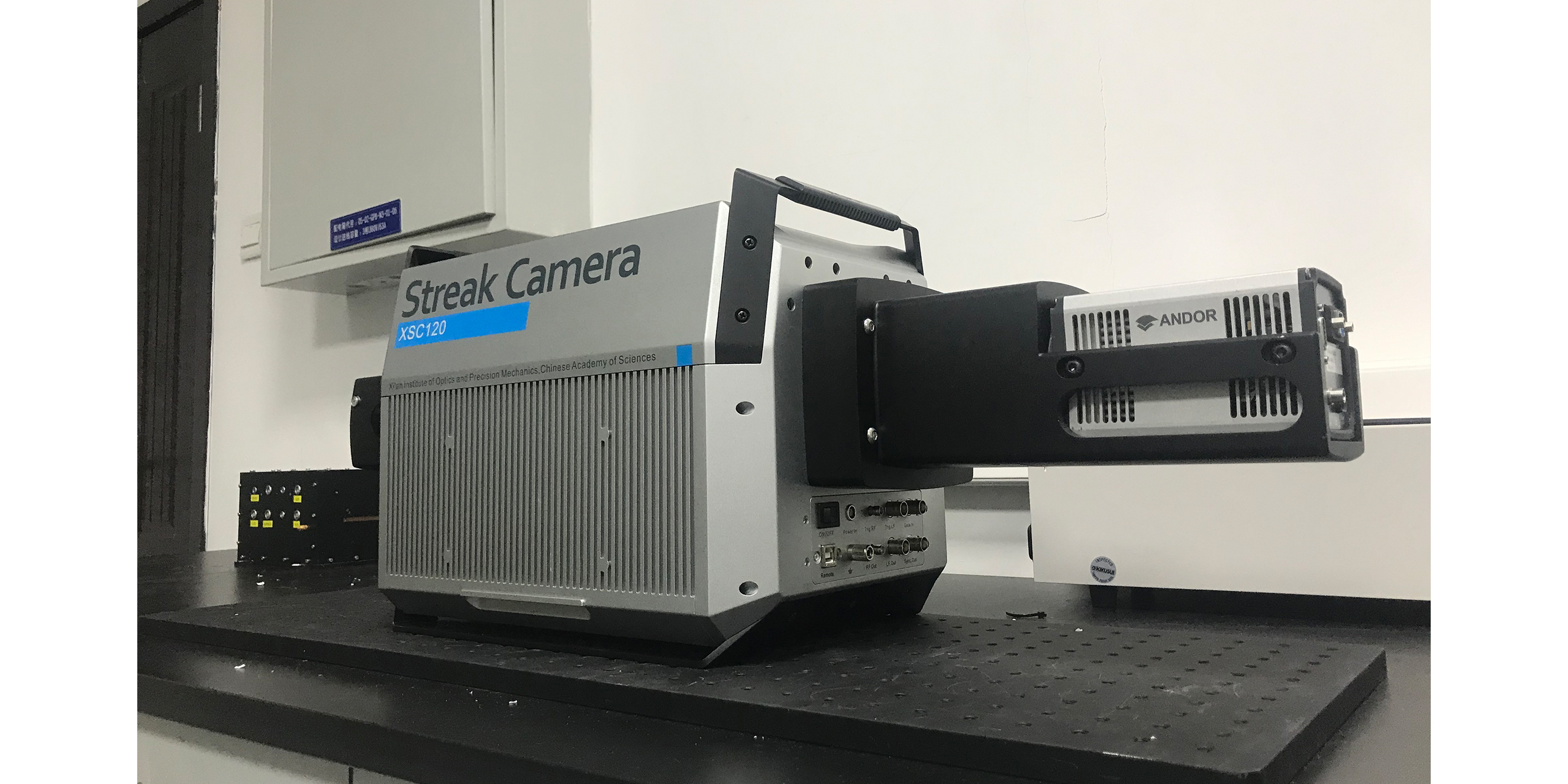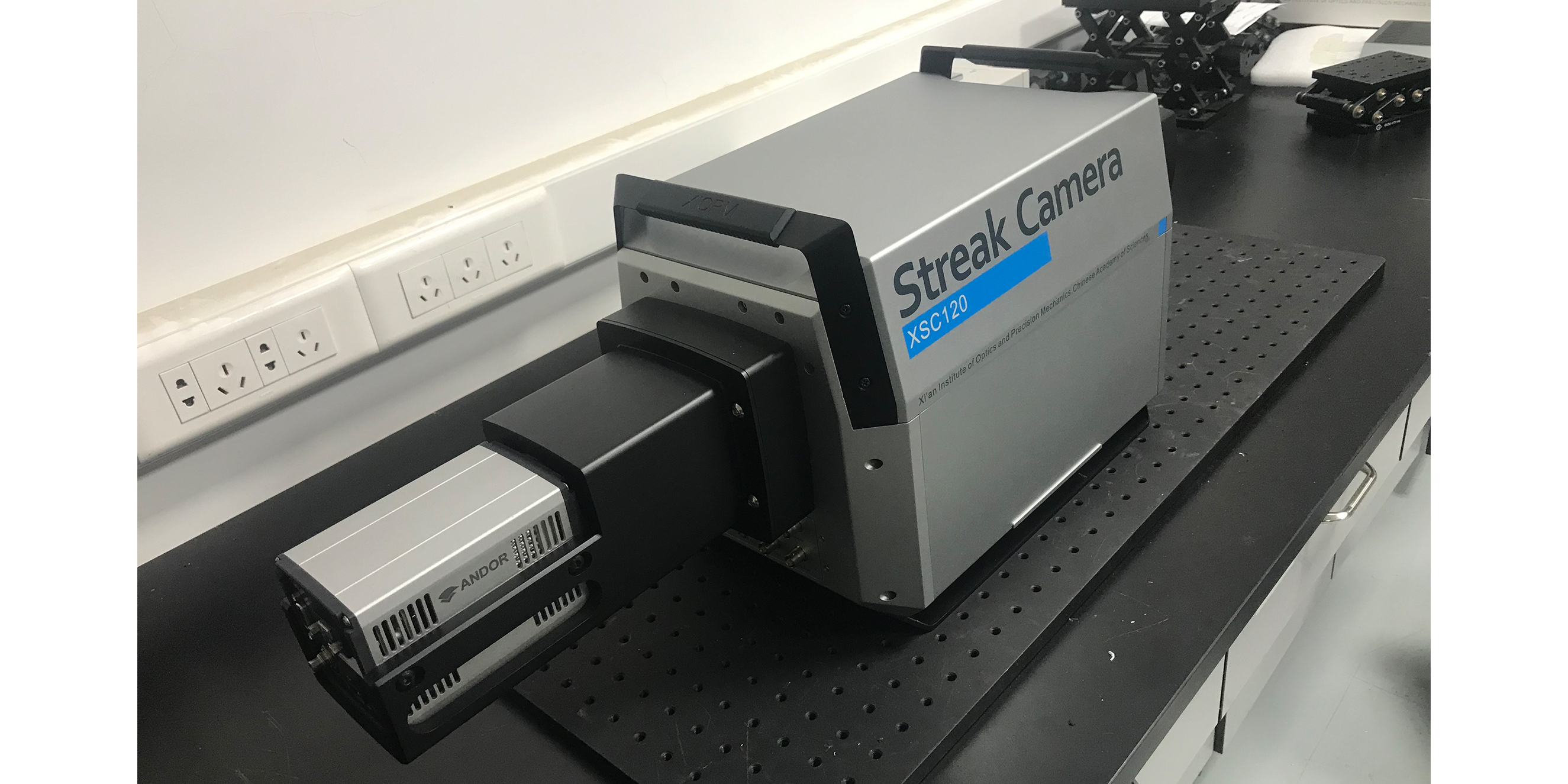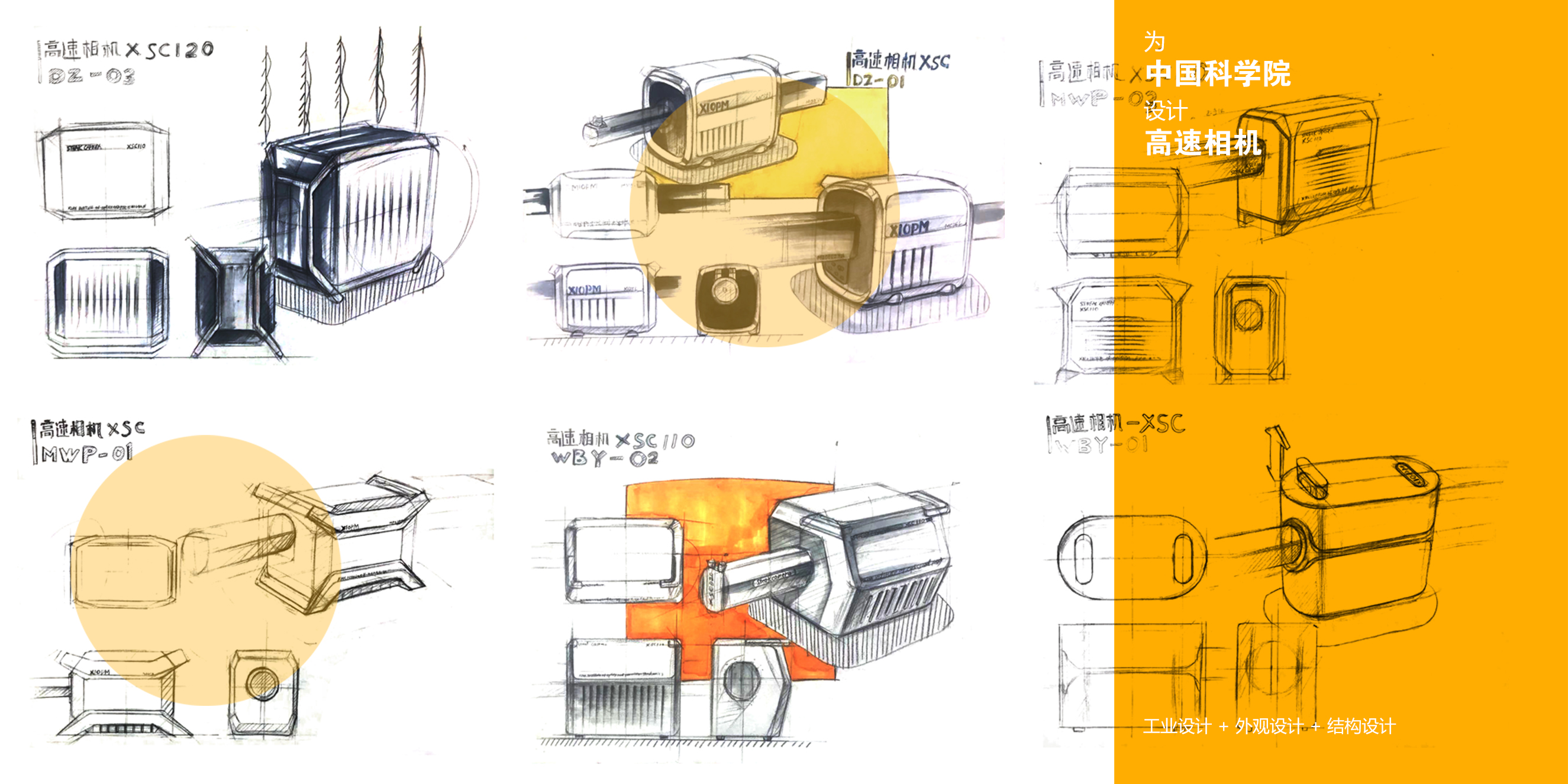
中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所(简称:西安光机所)创建于1962年,是中国科学院在西北地区最大的研究所之一。经过五十多年的创新历程,已经发展成为一个以战略高技术创新与应用基础研究为主的综合性科研基地型研究所。
西安光机所主要研究领域与方向:在基础光学领域主要研究方向为瞬态光学与光子学理论与技术;在空间光学领域主要研究方向为高分辨可见光空间信息获取和光学遥感技术、干涉光谱成像理论与技术;在光电工程领域,主要研究方向为高速光电信息获取与处理技术、先进光学仪器与水下光学技术。
研究所科研体系设有四大研究部,分别是基础科研部、光电技术部、空天技术部、先进制造部,下设26个研究单元,科研体系包括一个国家重点实验室、三个中科院重点实验室、两个陕西省工程技术中心、一个陕西省重点实验室,依托相应研究单元建设运行。并拥有完整的技术支撑体系。
Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM), Chinese Academy of Sciences was founded in 1962 and is one of the largest research institutes of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in the Northwest. After more than 50 years of innovation, it has developed into a comprehensive research base research institute focusing on strategic high-tech innovation and applied basic research.
The main research fields and directions of XIOPM are as follows: transient optics and photonics, high-resolution visible light spatial information acquisition and optical remote sensing technology, interference spectrum imaging, high-speed optoelectronic information acquisition and processing technology, advanced optical instruments and underwater optical technology.
The institute has 32 research units with complete technical service system, including one national key laboratory, three key laboratories of CAS, two Shaanxi Engineering and Technology Centers, one Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory and Xi’an Key Laboratory.








